Egypt History > Egyptian Dynasties
Egyptian Dynasties

Background
Early Dynastic Period
See Early Dynastic Period of Egypt.
Early Dynasties
Old Kingdom
See Old Kingdom of Egypt.
The Old Kingdom (2500-2100 BCE) was a period that first saw the development of the pyramids and featured some of the rulers of Egypt such as Khufu. During this period the rulers were despotic and centralized and have a massive bureaucracy. The kings word was law and the Egyptians did not develop a codified written set of laws. The kings continued the tradition of demanding taxes or tribute from all the nomes or provinces of the kingdom in order to create a surplus. During the First and Second Dynasties the kings would develop the mortuary complexes into the symbol of kingship. At first these were crude pyramids that eventually involved into a tradition that produced many dozen.
At this point the Egyptian kingdom was the largest nation in the ancient world. At this point the king was believed to have power of the Nile flooding, the rainfall along with all the people including foreigners. It was believed that god was not just the representation but the personification of the god of rightness named Ma'at.
Scribes were integral to this period as most of the population was illiterate farmers. Scribes were essential to maintain the massive bureaucracy and tax collection apparatus and there was a special school established in order to train scribes for careers in the army, palace, treasury or other institutions. The scribes were also involved in the supervision of the harvest and the irrigation projects.
There was known to have been an army of approximately 20,000 at the height of prosperity. It is believed that the Egyptians used slave labor for some public works and for domestic service. However, prisoners of war and foreign serfs had considerable rights in Egyptian society and could be involved in foreign affairs, rent and even cultivate land.
Khufu & the Great Pyramid
It was during this period that the tradition of pyramid building is believed to have been started. According to archaeologists they were ideological ladders to heaven, man-made mountains that would help guide the king to the afterlife. Later they become associated with the rays of the sun bursting through the clouds.
Khufu is credited with building the Great Pyramid of Giza however, there is no physical proof linking him to the construction of this monument. The entire city of Giza was one big sacred monument construction site and since stone is impossible to date unless there are inscriptions and artifacts it is hard to distinguish whose is whose. Oh, the archaeologists did not mention that no mummy has ever been found in the Great Pyramid and there are no engravings or inscriptions anywhere unlike 99.9% of every other Egyptian structure ever found?
Well the Egyptians believe that Thoth who was a king from Atlantis was responsible for their construction and he became deified in their early religion. According to them Thoth is also the creator of the Pillars of Hermes and the Emerald Tablet along with giving them wisdom, their language of hieroglyphs and so much more.
Until the Egyptian government lets more modern archaeologists excavate and examine the interior of the Great Pyramid we will never officially know who built it and for what purpose. The official answer is that it was a tomb or a monument but this makes absolutely no sense given the sheer size and energy required to build it and lack of all typical tomb or monument features. It could be an astro-archaeological monument given the precise calculations and measurements involved but again this could have been created on a smaller scale.
Old Kingdom Dynasties
First Intermediate Period
See First Intermediate Period of Egypt.
The First Intermediate Period (2181–2055 BCE) was a decline in the power of the monarchy and an increase in the power of the local leaders that occurred in Egyptian history. It is classified as a dark period that spanned about 125 years following the collapse of the Old Kingdom. This occurred when there began a period of great drought which also corresponded with a decrease in pyramid size. This indicates a loss of royal power and suggests the people may have grown discontent and began to blame the ineffective kings for the lack of flooding and crops. During this time the population growth rate was strained and famine began to plague Egypt.

Egyptian King, Court Official & Fanbearer - History of Costume (1880)
First Intermediate Dynasties
- 7th Dynasty of Egypt
- 8th Dynasty of Egypt
- 9th Dynasty of Egypt
- 10th Dynasty of Egypt
- Early 11th Dynasty of Egypt
Middle Kingdom
The Middle Kingdom is also called the Period of Reunification and occurs over between the last of the 11th dynasty and into the 12th. Some researchers believe it also includes the 13th and 14th dynasties of the Second Intermediate Period but this is debated. This unified kingdom was about to maintain a period of stasis that was eventually to pave way for the greatest dynasties Egypt had ever seen. During this period the god Osiris became heavily worshiped and every important in the Egyptian religion. By 1600 BCE to 1500 BCE there became disputes over heirs and economic and social instability which left Egypt prime for a new dynasty.
Middle Kingdom Dynasties
Second Intermediate Period
See Second Intermediate Period.
The Second Intermediate Period (1640-1530 BCE) marked the end of the Middle Kingdom and was a period of instability and economic disorder. There were many disputes over royal succession in this period which led the Hyksos to seize power in Lower Egypt. This period also corresponds with the Bronze Age Collapse in which nearly all of the civilizations in the Mediterranean and Mesopotamian regions were completely decimated.
Second Intermediate Dynasties
New Kingdom
See New Kingdom of Egypt.
New Kingdom Dynasties
Third Intermediate Period
See Third Intermediate Period.
The Third Intermediate Period is marked by the death of king Ramesses XI in 1070 BCE which ended the New Kingdom period of rule. This period like the other two intermediate periods is marked by political instability and this time by foreign conquest from more powerful neighbors.
26th Dynasty of Egypt (Nubians)
The Third Intermediate Period would end following the defeat of the Kushite rulers from Nubia of the 25th dynasty by the Assyrians. It would launch Egypt in an new age that marked the end of significant native Egyptian rule. Throughout the rest of antiquity and into the classical times the nation of Egypt would flourish as a culture but usually be ruled by a foreign empire.
Third Intermediate Dynasties
Late Period
See Late Period of Egypt.
Achaemenid Empire
Egypt was later conquered in 525 BCE by the Achaemenid Empire. The invasion was led by the son of Cyrus the Great named Cambyses II who would later die during an engagement.
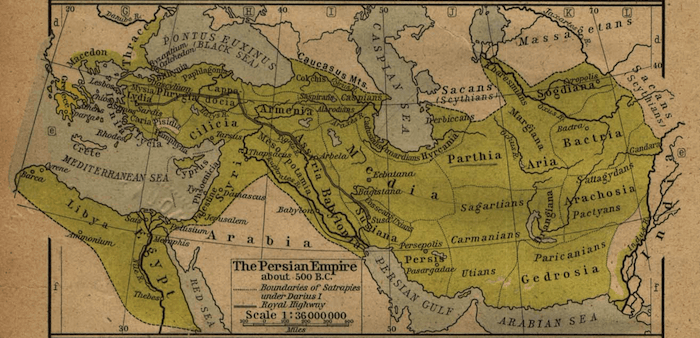
Achaemenid Empire (500 BCE) - Historical Atlas (1923)
In 404 BCE the 28th Dynasty was established by Amyrtaeus, the prince of Sais who rebelled against the Achaemenids. He built no monuments with his name and only ruled for six years before the 29th Dynasty under Mendes took control until 380 BCE. The 30th Dynasty was a series of three kings that ruled from 380 BCE until 343 BCE when they were finally re-occupied by the Persians. This resulted in the Second Achaemenid Period of the 31st Dynasty which lasted from 343 BCE until Alexander the Great liberated Egypt in 332 BC.
Late Period Dynasties
- 26th Dynasty of Egypt
- 27th Dynasty of Egypt
- 28th Dynasty of Egypt
- 29th Dynasty of Egypt
- 30th Dynasty of Egypt
- 31st Dynasty of Egypt
Greco-Roman Egypt
Dynasties of Ancient EgyptAll years (rightmost column) are BC (BCE)pre-historyEarly[show]Old Kingdom[show]First Intermediate[show]Middle Kingdom[show]Second Intermediate[show]New Kingdom[show]Third Intermediate[show]Late Period[show]Ptolemaic (Hellenistic)[show]| Dynasty | Years | Kingdom |
| First Dynasty (I) | 3150–2890 | |
| Second Dynasty | 2890–2686 |
Egyptian Dynasties
Egyptian Dynasties List
Old Kingdom of Egypt
First Intermediate Period of Egypt
- Seventh Dynasty of Egypt
- Eighth Dynasty of Egypt
- Ninth Dynasty of Egypt
- Tenth Dynasty of Egypt
- Early Eleventh Dynasty of Egypt
Middle Kingdom of Egypt
- Late Eleventh Dynasty of Egypt
- Twelfth Dynasty of Egypt
- Thirteenth Dynasty of Egypt
- Fourteenth Dynasty of Egypt
Second Intermediate Period
- Fifteenth Dynasty of Egypt
- Sixteenth Dynasty of Egypt
- Abydos Dynasty of Egypt
- Seventeenth Dynasty of Egypt